// Comment
//Inputs:
int[] denoms = {25,10,5,1};
int[][] map = new int[100+1][denoms.length];
System.out.println(makeChange(100, denoms, 0));
System.out.println(makeChangeDP(100, denoms, 0, map));
// Recursive algorithm
public static int makeChange(int amount, int[] denoms, int index)
{
if(index >= denoms.length-1) return 1;
int denomAmount = denoms[index];
int ways = 0;
for(int i = 0; i*denomAmount <= amount; i++)
{
int amountRemaining = amount-i*denomAmount;
ways += makeChange(amountRemaining, denoms, index+1);
}
return ways;
}
// Dynamic programming.. map[amount+1][denoms.length]
public static int makeChangeDP(int amount, int[] denoms, int index, int[][] map)
{
if(map[amount][index] != 0) return map[amount][index];
if(index >= denoms.length-1) return 1;
int denomAmount = denoms[index];
int ways = 0;
for(int i = 0; i*denomAmount <= amount; i++)
{
int amountRemaining = amount-i*denomAmount;
ways += makeChange(amountRemaining, denoms, index+1);
}
map[amount][index] = ways;
return ways;
}
Data Structure & Algorithm_Array - JAVA
Saturday, September 6, 2014
Coin change problem
Thursday, September 4, 2014
Quick sort in Java
// Comment Quick Sort
public static void quick_sort(int[] a) {
int len = a.length;
if (a == null || len == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Null/Invalid Input");
quick_sortUtil(a, 0, len - 1);
}
private static void quick_sortUtil(int[] a, int l, int r) {
if (l > r)
return;
int p = pivot(a, l, r);
quick_sortUtil(a, l, p - 1);
quick_sortUtil(a, p + 1, r);
}
private static int pivot(int[] a, int l, int r) {
int x = a[r], j, i;
for (i = l, j = l; i < r && j < r; i++) {
if (a[i] <= x) {
swapArr(a, i, j);
j++;
}
}
swapArr(a, j, r);
return j;
}
private static void swapArr(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
Tets
// Comment
public class Testing {
public Testing() {
}
public void Method() {
/* Another Comment
on multiple lines */
int x = 9;
}
}
Merge sort in JAVA : Top-down implementation using lists
// Comment Merge Sort for array
public static void mergeSort(int[] A) {
if (A == null)
throw new NullPointerException("Input doesn't exist.");
int len = A.length;
if (len == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No input from user.");
mergeSortUtil(A, 0, len - 1);
}
private static void mergeSortUtil(int[] a, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r)
return;
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
mergeSortUtil(a, l, m);
mergeSortUtil(a, m + 1, r);
merge(a, l, m, r);
}
private static void merge(int[] a, int l, int m, int r) {
int k = 0, i, j;
int[] b = new int[(r - l) + 1];
for (i = l, j = m + 1; i <= m && j <= r;) {
if (a[i] < a[j])
b[k++] = a[i++];
else
b[k++] = a[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
b[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= r)
b[k++] = a[j++];
for (int s = l, f = 0; f < b.length; s++) {
a[s] = b[f++];
}
}
Top-down implementation using lists :
function merge_sort(list m)
// Base case. A list of zero or one elements is sorted, by definition.
if length(m) <= 1
return m
// Recursive case. First, *divide* the list into equal-sized sublists.
var list left, right
var integer middle = length(m) / 2
for each x in m before middle
add x to left
for each x in m after or equal middle
add x to right
// Recursively sort both sublists.
left = merge_sort(left)
right = merge_sort(right)
// *Conquer*: merge the now-sorted sublists.
return merge(left, right)
In this example, the
merge function merges the left and right sublists.function merge(left, right)
var list result
// assign the element of the sublists to 'result' variable until there is no element to merge.
while length(left) > 0 or length(right) > 0
if length(left) > 0 and length(right) > 0
// compare the first two element, which is the small one, of each two sublists.
if first(left) <= first(right)
append first(left) to result
left = rest(left)
else
append first(right) to result
right = rest(right)
else if length(left) > 0
append first(left) to result
left = rest(left)
else if length(right) > 0
append first(right) to result
right = rest(right)
end while
return result
public static LNode mergeSortList(LNode list) {
int len = length(list);
if (len <= 1)
return list;
LNode left = list, right = null;
right = addLeftList(left, len);
left = mergeSortList(left);
right = mergeSortList(right);
LNode res = merge(left, right);
return res;
}
private static int length(LNode list) {
int len = 0;
for (LNode curr = list; curr != null; curr = curr.next)
len++;
return len;
}
private static LNode addLeftList(LNode list, int n) {
int m = n / 2;
LNode curr = list;
for (int i = 0; curr != null && i < m - 1; i++)
curr = curr.next;
list = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
return list;
}
private static LNode merge(LNode left, LNode right) {
LNode result = null, curr = null, tmp = null;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
curr = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
curr = right;
right = right.next;
}
if (result == null) {
result = curr;
tmp = curr;
} else {
tmp.next = curr;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if (left != null)
tmp.next = left;
if (right != null)
tmp.next = right;
return result;
}
Monday, August 18, 2014
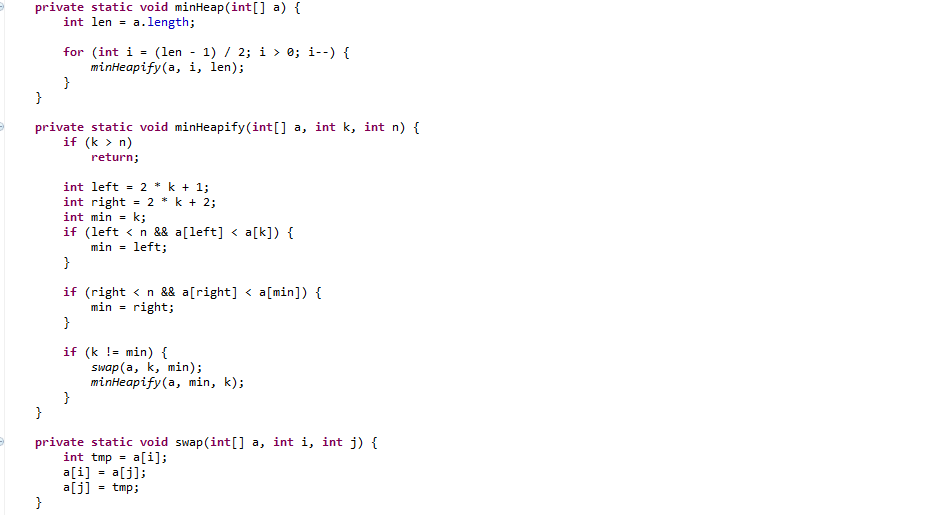
Connect n ropes with minimum cost: JAVA
Following is complete algorithm for finding the minimum cost for connecting n ropes.
Let there be n ropes of lengths stored in an array len[0..n-1]
1) Create a min heap and insert all lengths into the min heap.
2) Do following while number of elements in min heap is not one.
……a) Extract the minimum and second minimum from min heap
……b) Add the above two extracted values and insert the added value to the min-heap.
3) Return the value of only left item in min heap.
For 5,6,7,8 is 11+15+26=52 and not 55.
References:
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/connect-n-ropes-minimum-cost/
Let there be n ropes of lengths stored in an array len[0..n-1]
1) Create a min heap and insert all lengths into the min heap.
2) Do following while number of elements in min heap is not one.
……a) Extract the minimum and second minimum from min heap
……b) Add the above two extracted values and insert the added value to the min-heap.
3) Return the value of only left item in min heap.
For 5,6,7,8 is 11+15+26=52 and not 55.
References:
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/connect-n-ropes-minimum-cost/
Saturday, July 19, 2014
Maximum Sum Path in Two Arrays
Program:
Reference:
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/maximum-sum-path-across-two-arrays/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)